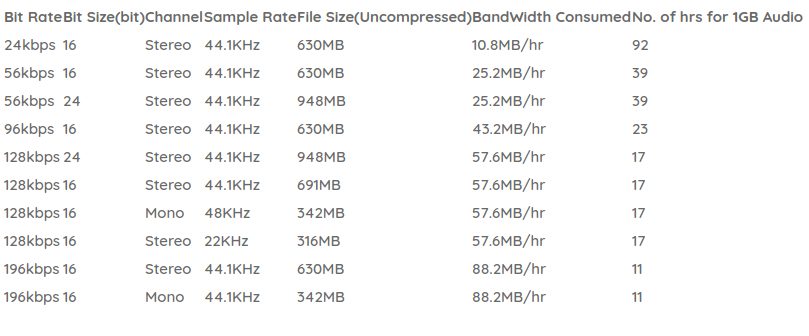
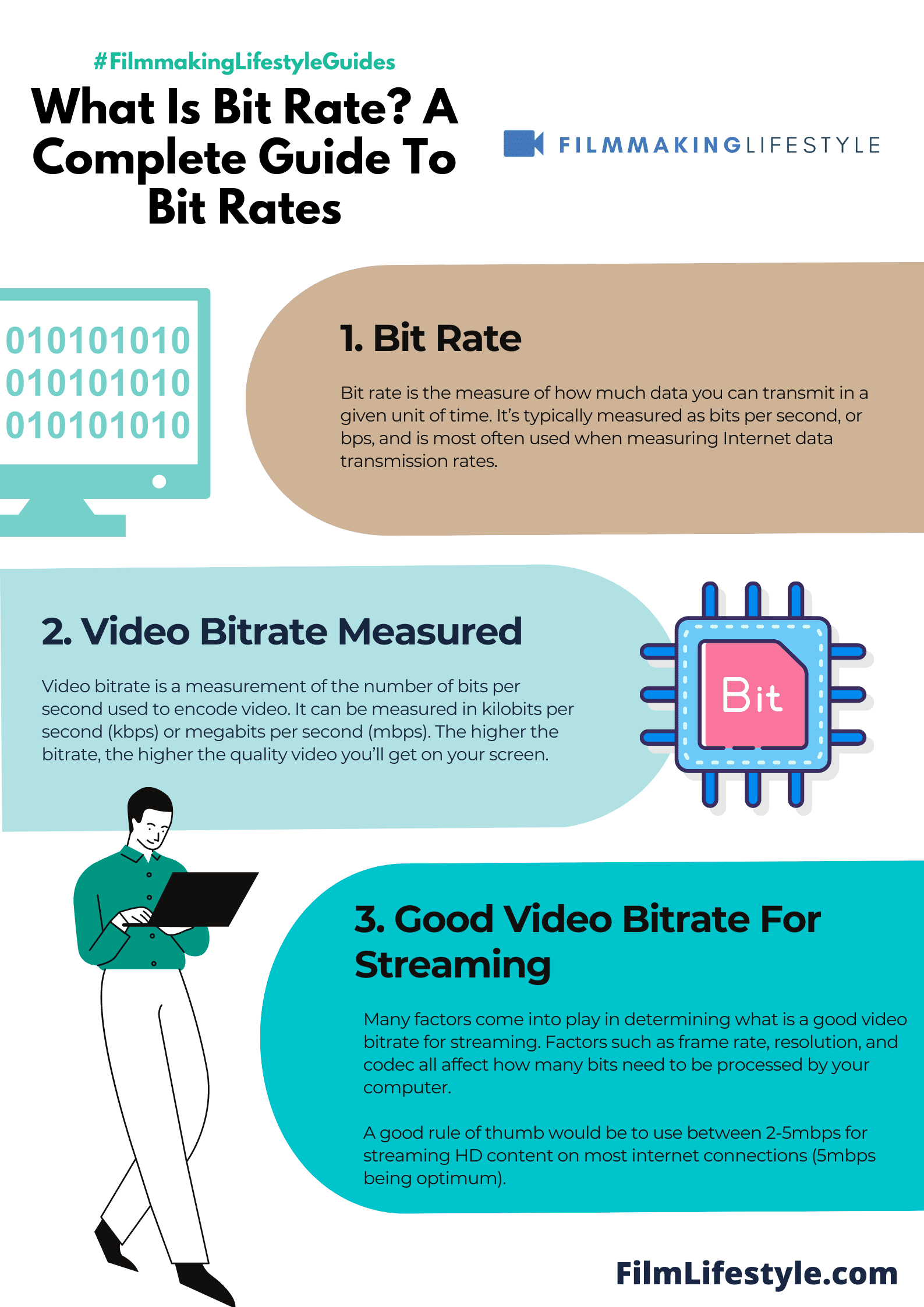
Video bitrate is the number of bits that are processed in one second. It’s mainly used to measure how much data a computer or device can handle at any given time, and it’s measured in kilobits per second (kbps). One kb equals 1024 bytes.
Video bitrates are crucial because they determine file size, video quality, and streaming performance for online videos.
If you’re using an old phone with limited storage space or have a slow internet connection, then you’ll want to set your video resolution as low as possible so that it doesn’t take up too much memory on your device and buffer during playback.
This is usually measured in megabits per second (Mbps).
The higher the video bitrate, the larger and more detailed your video will appear.
For example, when watching a YouTube video on a slow internet connection you may notice that it appears blocky or pixelated. This is because YouTube automatically adjusts to lower-quality videos if it senses that you’re not getting enough bandwidth.
If you are streaming HD content from Netflix though, they will provide an HD stream even if your internet speed isn’t great as long as you have at least 3Mbps available for viewing purposes. Video Bitrates range anywhere between 300Kbps – 2Mbps with 720p.
WHAT IS BIT RATE
What Is Bit Rate?
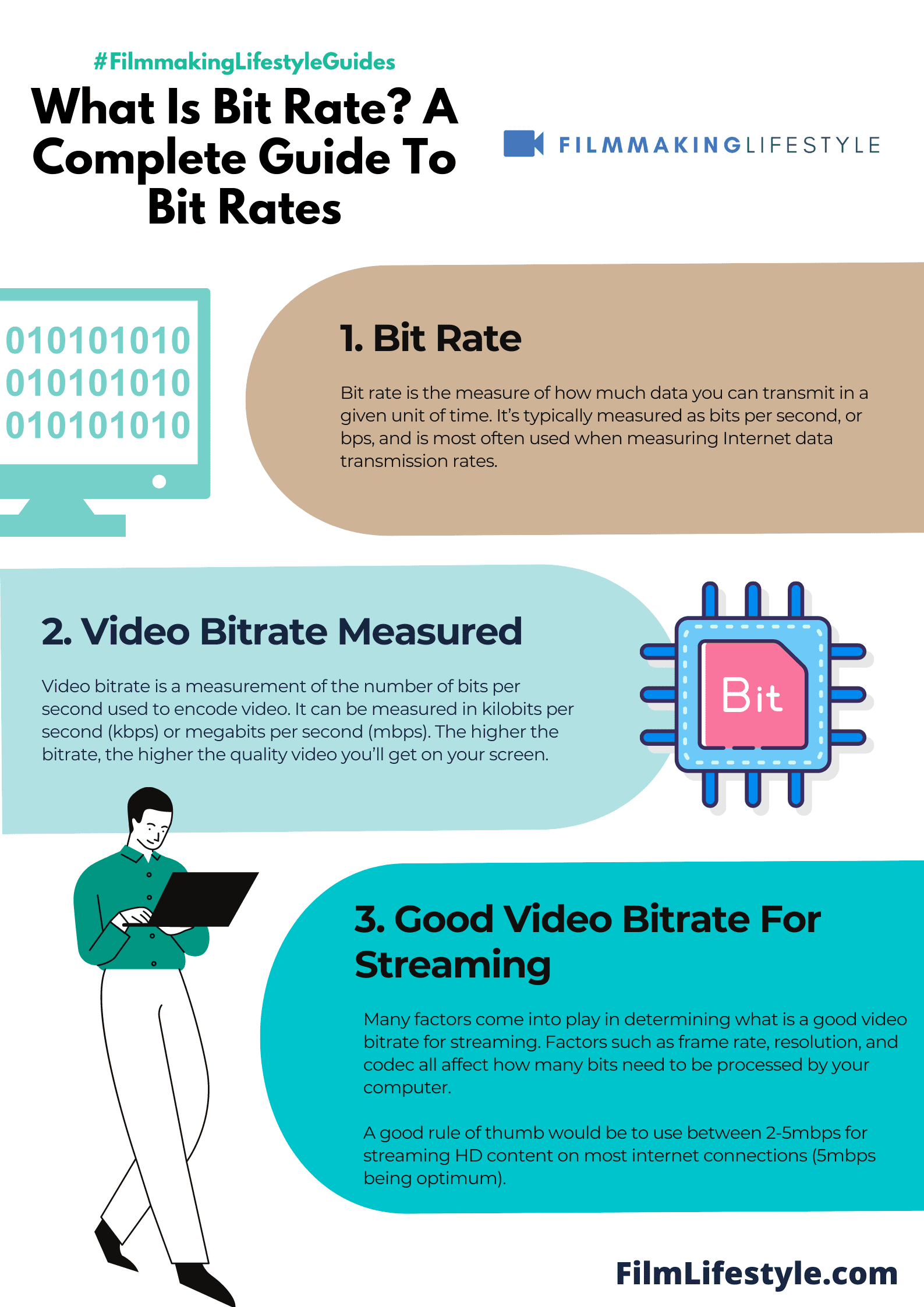
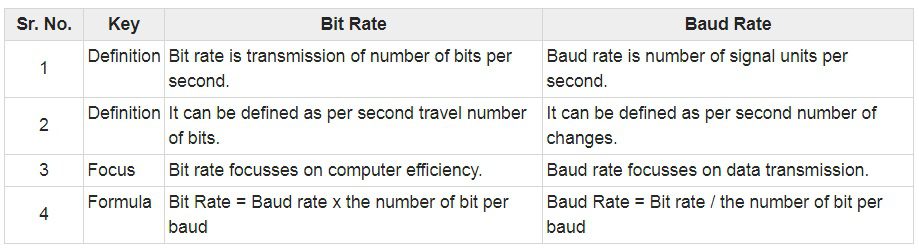
Bit rate is the measure of how much data you can transmit in a given unit of time. It’s typically measured as bits per second, or bps, and is most often used when measuring Internet data transmission rates.
The bit rate for an internet connection varies depending on the type of connection being used to access the internet.
A dial-up modem has one speed (56kbps), while DSL connections have three speeds: 1Mbps, 2Mbps, and 3Mbps. Cable modems are faster still at 8Mbit/s downstream and 4Mbit/s upstream, and fiber optic connections make up the fastest group with 100Mbit/s downstream and 10 Mbit/s upstream bit rates.
Ever wondered why some videos look crystal clear while others seem to lag or blur?
It’s all about the bit rate, a crucial factor in digital media quality that we’ll dive deep into today.
Understanding bit rate is key to mastering media files, whether you’re streaming your favorite show or fine-tuning a video project.
We’ll unpack everything you need to know, ensuring you’re equipped to make the best choices for your digital media experience.
What Is Bit Rate?
When diving into the technicalities of digital media, it’s imperative to understand bit rate.
Bit rate is the rate at which data is processed or transferred, often measured in megabits per second (Mbps) or kilobits per second (Kbps).
For us filmmakers, bit rate is the backbone of video quality.
A higher bit rate typically translates to better video quality because more data is used to represent each second of the footage.
Key Factors Influencing Bit Rate
Several factors dictate the bit rate of a video file:
- Resolution – Higher resolutions like 4K or 1080p require higher bit rates to maintain clarity.
- Frame Rate – Videos with higher frame rates such as 60fps demand more data flow to remain smooth.
- Compression – Compressed files sacrifice some data, potentially lowering the bit rate and altering quality.
Understanding bit rate is crucial when exporting our projects.
Choices made during this stage can have a lasting impact on the visual experience of our audience.
A common misstep is underestimating the importance of bit rate in audio quality.
Just like with video, audio with a higher bit rate means a fuller, more detailed sound.
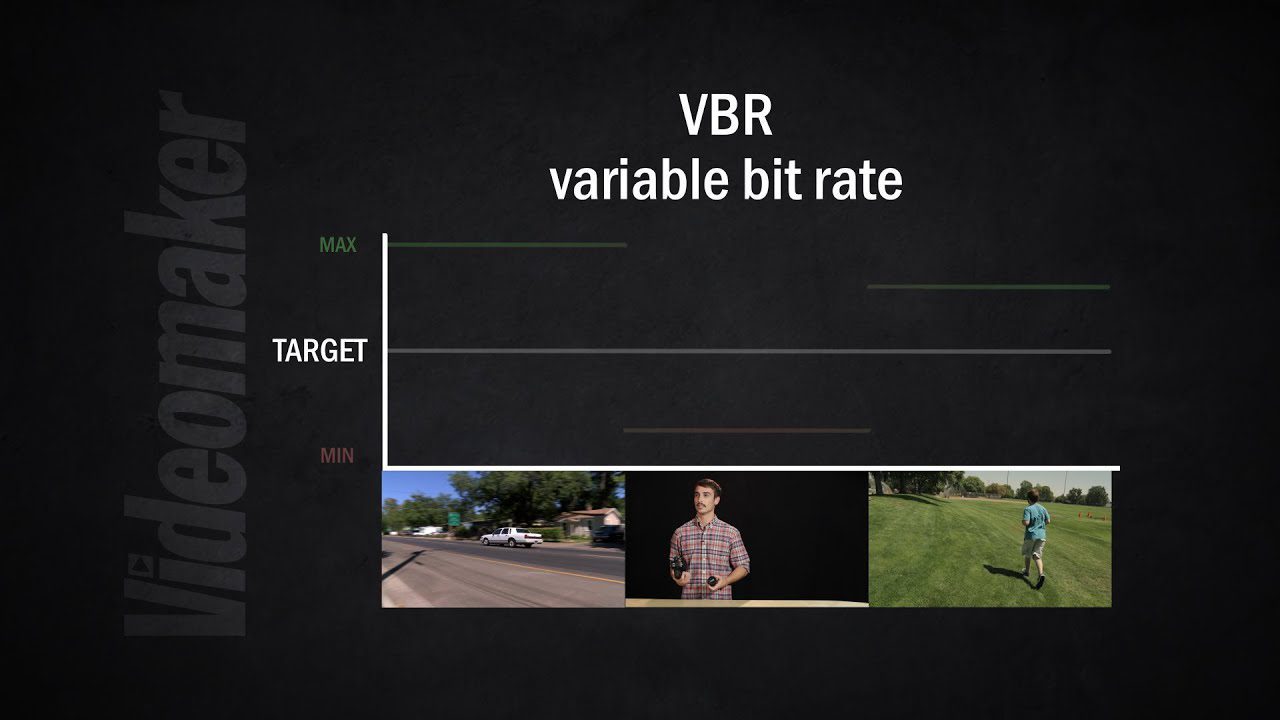
When streaming, the available bandwidth also comes into play.
Services dynamically adjust video bit rates to ensure continuous playback, which affects the viewing experience.
When working on video projects, we’re often faced with the challenge of balancing file size and quality.
Striking this balance involves a thorough grasp of bit rates and the factors that influence them.
In the film industry, standard bit rate practices can vary.
Blockbusters, such as Inception or The Avengers, often have significantly higher bit rates compared to independent movies, allowing for a richer visual and aural experience.
Considering all these factors, it becomes clear that bit rate is a critical element in the quest for cinematic perfection.
As content creators, our aim is to provide viewers with the utmost visual and auditory delight, and mastering bit rates allows us to inch closer to that goal.
Why Is Bit Rate Important In Digital Media?
When we talk about digital media, bit rate is a cornerstone metric that directly impacts the quality of the content we produce and consume.
Understanding the significance of bit rate is crucial for anyone involved in filmmaking or video content creation.
A higher bit rate typically means there’s more data to represent our audiovisuals, leading to clearer and more detailed images and sounds.
This is especially important for us in filmmaking, where every frame counts towards storytelling and mood setting.
Several factors highlight the importance of bit rate:
- Detail and Clarity – A higher bit rate can result in less compression, preserving fine details that enhance visual appeal. Think about the texture of clothing in Parasite or the scenic vistas in The Revenant.
- File Size and Streaming – Bit rate directly affects file size. For streaming services, managing this is critical to providing smooth playback without buffering, leading to a better user experience.
- Compression Artifacts – Lower bit rates often lead to noticeable compression artifacts such as banding or pixilation. Maintaining an optimal bit rate is pivotal in avoiding these issues.
In our quest to deliver top-notch video content, gauging the right bit rate is a balancing act – weighing the quality against file size and transmission requirements.
In the realm of digital media, bit rate is a key determinant of whether a video looks professionally crafted or amateurish.
For us as content creators, it’s also about knowing our audience’s expectations.
With the evolution of technology, viewers are becoming more discerning, and skimping on bit rate can be the difference between commanding attention and being overlooked.
finally, the choice of bit rate also affects post-production flexibility.
If we’re aiming for massive color grading or other editing adjustments, higher bit rates give us the necessary data for those refinements.
It’s the difference between having the room to enhance visual storytelling or being constrained by data limitations.
How Does Bit Rate Affect Video Quality?
Video quality is deeply intertwined with bit rate.
Higher bit rates generally mean more data is used to encode the video, which translates to better picture quality.
Lower bit rates, on the other hand, often result in reduced clarity and visible compression artifacts, such as pixelation or motion blur.
The relationship between bit rate and video resolution is critical to understand.
While high-resolution videos like 4K or 1080p have the potential for stunning visuals, they require adequate bit rates to maintain their quality.
Without a high enough bit rate, even these sharp resolutions can look subpar.
We must also consider the frame rate.
A video with a high frame rate – think action-packed scenes from Mad Max: Fury Road – needs a higher bit rate to maintain quality across all those frames.
Otherwise, movement can appear jerky or smeared, detracting from the viewer’s experience.
Color depth is another factor impacted by bit rate:
- Rich, vivid colors require a higher bit rate to be accurately represented – Gradients can display banding with insufficient bit rates,
- Scenes with complex color schemes, such as those found in Avatar, are especially dependent on a sufficient bit rate to prevent color degradation.
eventually, bit rate is a balancing act.
For filmmakers, it’s finding that sweet spot where video quality meets file size and streaming capability without compromising on the visual storytelling.
We always strive to optimize bit rate to ensure our audiences receive the best viewing experience our resources allow.
How To Calculate Bit Rate?
Calculating bit rate is essential for ensuring that our videos maintain the intended quality while also being manageable in size.
It’s a straightforward process that requires some basic information about the video file.
Firstly, we need to know three key factors – the video’s frame rate, resolution, and color depth.
These directly influence the size and quality of our video:
- Frame rate is measured in frames per second (fps) and represents how many individual frames are shown each second.
- Resolution describes the number of pixels in each dimension that the video contains.
- Color depth, often measured in bits, indicates how many bits are used to represent the color of a single pixel.
Knowing these details, we can use the following formula to calculate bit rate: Bit rate (bps) = frame rate × resolution × color depth.
But, this will give us the raw bit rate before any compression.
If we’re using compressed video formats, such as H.
264 or HEVC, the actual bit rate will be lower due to the efficiency of the codec.
When working with compressed video, it’s crucial to consider the codec’s compression ratio.
Each codec compresses video data differently, impacting the final bit rate.
Factors like motion complexity and the type of content also play a part.
To account for compression, we can adjust the raw bit rate with an estimated compression factor for our chosen codec.
For example, a compression factor of 0.
2 for highly efficient compression or 0.
8 for less compression could be applied, leading to a more accurate bit rate estimation for our files.
Note: It’s vital to remember that these calculations are an approximation.
The actual bit rate might vary based on encoding settings and the content’s complexity.
What Is Bit Rate – Wrap Up
We’ve delved into the nuances of bit rate and its pivotal role in shaping the quality of digital media.
As we’ve seen, striking the right balance is key to delivering content that meets both the technical and aesthetic standards of our audience.
Remember, while our calculations give us a solid starting point, the true test lies in the final output.
It’s up to us to tweak and fine-tune our settings to perfection, ensuring our media not only looks and sounds great but also aligns with the practicalities of distribution and storage.
Let’s keep pushing the boundaries of digital excellence, one bit at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Bit Rate And Why Is It Important In Digital Media?
Bit rate is the amount of data processed per unit of time in digital media, affecting the quality of audiovisual content.
A higher bit rate means clearer, more detailed images and sounds, which is crucial for maintaining content quality and avoiding compression artifacts.
How Does Bit Rate Impact File Size And Streaming?
The bit rate directly influences file size; a higher bit rate results in larger files.
For streaming, a higher bit rate requires more bandwidth but delivers better quality.
Balancing bit rate is key for optimal streaming performance without excessive buffering.
What Should Content Creators Know About Bit Rate?
Content creators should understand how bit rate affects the quality and file size of their media.
Choosing the right bit rate involves considering the audience’s expectations and the desired quality of the video to be produced.
How Can One Calculate The Bit Rate For A Video?
To calculate video bit rate, consider factors like frame rate, resolution, and color depth.
Multiply these factors to get a raw bit rate estimation, adjusting for compression formats and desired quality.
Does Compression Affect The Actual Bit Rate Of A Video?
Yes, compression significantly impacts the actual bit rate of a video.
It reduces the bit rate by removing redundant or unnecessary data, but excessive compression can lead to loss of quality.
Are Bit Rate Calculations Always Accurate?
No, bit rate calculations are approximations that provide a baseline figure.
Actual bit rates can differ due to encoding settings and the complexity of the content being encoded.
Adjustments may be necessary after initial calculations.