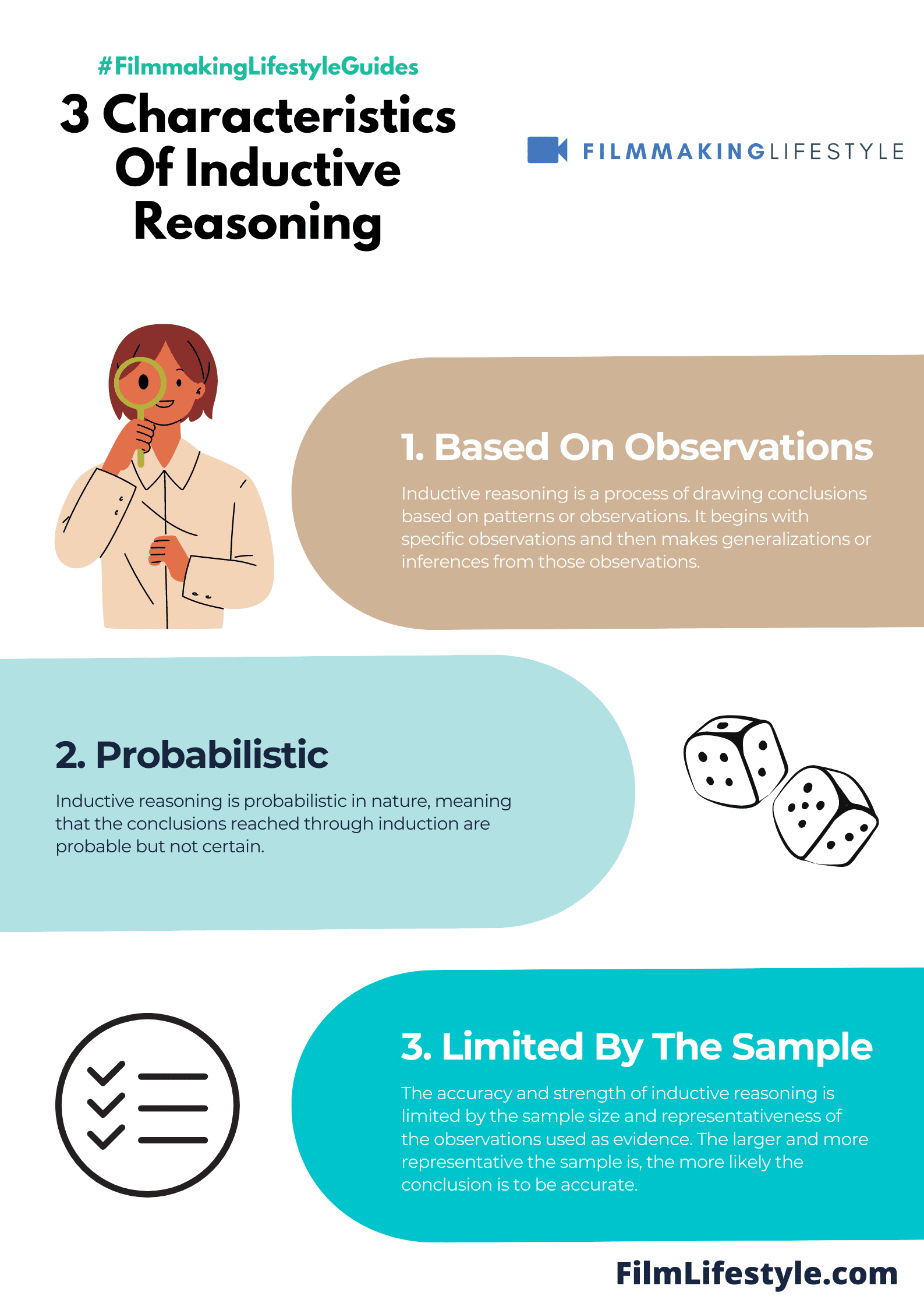
The scientific method is largely based on inductive reasoning. You begin by studying a small sample population and then extrapolate your findings to apply to a larger group or population as a whole.
Inductive reasoning is the process of drawing conclusions from specific observations.
It can be contrasted with deductive reasoning, which starts with general principles and draws specific conclusions.
Also known as induction, inductive reasoning is a key component in scientific discovery and hypothesis formation.
inductive reasoning
What Is inductive reasoning?
Inductive reasoning is the process of using a sample to draw conclusions about a larger group or population.
Inductive reasoning is based on observation and information processing, rather than logic and theory.
In other words, you use facts that you know for sure to come up with an idea about something else that you can’t be certain about.
This form of reasoning is often used in science to come up with theories based on known facts.
Inductive reasoning is our mental shortcut to making sense of patterns and forming conclusions from incomplete information.
It’s how we often predict the future based on past experiences, without needing airtight evidence.
We’ll jump into the nuts and bolts of inductive reasoning, exploring its role in everyday decision-making and scientific discovery.
Stick with us to unlock the secrets of this critical thinking skill that shapes our understanding of the world around us.
What Is Inductive Reasoning
Inductive reasoning allows us to process information and make predictions about what might happen next.
It’s how we form hypotheses and anticipate outcomes based on observations.
It involves looking at specific instances and drawing a general conclusion from them.
When a filmmaker sees that films with strong character development tend to be more engaging, they might apply this idea to their own projects.
This form of reasoning is not purely black and white.
It relies heavily on the probability of an outcome rather than certainty.
As creative professionals, we often use inductive reasoning to guess an audience’s reaction to a new film based on past trends.
We identify patterns, infer meanings, and create narratives that resonate with viewers.
With each new piece of work, filmmakers add to a larger understanding of what connects with audiences.
When we make decisions on set or during post-production, inductive reasoning guides us –
- Selecting the right angle for a shot to tell a story effectively,
- Deciding how to cut scenes together to maintain suspense.
Recognizing the role of inductive reasoning helps us improve our artistic intuition.
The process feeds into how we craft stories and how we pursue innovation in filmmaking.
Our understanding of inductive reasoning enhances with each project we tackle.
New evidence collected from these projects refines our ability to predict future successes.
Even though its imperfections, inductive reasoning remains a staple in the filmmaker’s toolkit.
As we encounter a myriad of outcomes, we’re reminded that while patterns can guide us, there’s always room for the novel and unexpected.
How Inductive Reasoning Works
Inductive reasoning is an integral process that drives the creative and decision-making aspects of filmmaking.
It begins with observing the small details and patterns within various film elements.
These observations lead to broader generalizations that inform future film projects.
From camera angles to lighting techniques, every decision is a piece of a larger puzzle.
Cinematographers, for instance, might notice how certain lighting setups evoke a specific mood in audiences.
Based on this, they develop lighting schemes predicted to elicit desired emotional responses in new films.
Directors often rely on their understanding of character development trends to shape performances.
This can involve nuancing an actor’s portrayal or adjusting the narrative flow to better capture audience engagement.
Editors play a crucial role, employing inductive reasoning to determine the pacing and rhythm that best tells a story.
They analyze past successful editing patterns and apply them to ensure the current project resonates with viewers.
When it’s time to market a film, inductive reasoning guides the creation of promotional materials.
Marketers look at what has captured attention in film trailers and social media campaigns and craft their strategy accordingly.
Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
- Gather specific instances or relevant events,
- Detect patterns and regularities within those instances,
- Formulate hypotheses based on observed patterns,
- Apply these generalized principles to new situations or projects.
This method isn’t without its risks.
Predictions made from inductive reasoning can lead us astray if the observed instances aren’t representative.
We recognize its limitations while valuing its power to inspire innovation in our art.
The Role Of Inductive Reasoning In Everyday Decision-making
Inductive reasoning isn’t just a film industry tool.
It plays a crucial role in the choices we make daily.
From simple decisions like what to wear based on the weather patterns to more complex ones like choosing a career path by observing industry trends, we’re constantly using inductive reasoning.
This form of reasoning helps us navigate life’s unpredictability.
We might not always be aware, but inductive reasoning allows us to learn from past experiences and make informed guesses about the future.
For instance, if a director has had success with a particular genre, they might lean towards similar projects expecting similar outcomes.
In the realm of digital marketing, inductive reasoning is key to understanding consumer behavior.
Marketers analyze data from past campaigns – what drove the most engagement, which platforms had the highest ROI, or what content garnered the most attention.
From these specifics, they derive broader strategies tailored for future marketing efforts.
The impact of inductive reasoning extends to the technical aspects of filmmaking as well:
- Editors might review footage and discern the most impactful takes to craft a compelling narrative.
- Cinematographers could decide on lighting techniques that are influenced by the emotional tone of previously successful scenes.
This reasoning approach is also invaluable for on-the-spot decision-making.
For instance, during filming, if a certain shot isn’t working, the crew might draw from previous experiences to quickly adapt and find a solution without the need for extensive deliberation.
Understanding the subtleties of inductive reasoning enriches decision-making.
Whether we’re facing a set of variables on set or sifting through market data, we use the patterns of the past to steer the choices of the present.
So, we continuously hone this skill, aware of its power to influence both the minute details and the overarching strategies that define our creative, professional, and personal lives.
Examples Of Inductive Reasoning In Real Life
Inductive reasoning transcends the boundaries of professional fields and enters the realm of our daily activities.
Let’s look at some common instances where we, often unknowingly, apply inductive reasoning in day-to-day life.
Every time we meet someone new, we automatically use past experiences to form an initial impression.
This is inductive reasoning at work, where we compile various social cues and verbal communication to gauge a person’s character.
Much of our decision-making follows a pattern that stems from previously gathered information.
For instance, when choosing what film to watch next, we might consider critically acclaimed works or genres that we’ve enjoyed in the past.
Here are some areas where inductive reasoning unknowingly plays a pivotal role:
- Consumer Choices – decisions on purchases are frequently led by reviews and recommendations,
- Health Practices – adopting diets and exercise regimes based on success stories,
- Parenting Strategies – using what has proven effective for others in raising children.
In the professional sphere, inductive reasoning becomes even more
Business strategies are often developed by analyzing market trends and customer feedback, aiming to predict and cater to future demand.
The art of filmmaking itself is steeped in inductive reasoning.
From scripting to production, decisions are influenced by audience preferences and past box office successes.
When a particular style of cinematography receives widespread acclaim, it’s not unusual for us to apply similar techniques in upcoming projects, expecting comparable results.
Identifying patterns in customer behavior is a staple in digital marketing.
We scrutinize click-through rates, engagement metrics, and consumer demographics to tailor our strategies, fostering an environment where businesses and creativity flourish side by side.
While we may not always label our thought processes as inductive reasoning, it’s evident that our actions and choices are frequently guided by this method of logical inference.
By understanding and harnessing its power, we enhance not only our professional endeavors but our personal lives as well.
Inductive Reasoning In Scientific Discovery
Inductive reasoning serves as a cornerstone in the quest for scientific knowledge.
By observing patterns, forming hypotheses, and conducting experiments, scientists use inductive reasoning to develop new theories.
The progression from hypothesis to theory often seems linear, but it’s a complex web of trials, errors, and insights.
This methodical approach underpins the majority of our scientific achievements, leading to landmark discoveries and technological advancements.
In the realm of physics, inductive reasoning helped Albert Einstein develop the theory of relativity.
By examining existing evidence and applying creative thought, he was able to conceive a framework that revolutionized our understanding of time and space.
The field of medicine also benefits greatly from inductive reasoning.
Researchers analyze patterns in patient data to uncover links between behaviors and health outcomes, leading to breakthroughs in treatments and preventative measures.
Consider the following examples where inductive reasoning played a pivotal role in scientific discovery:
- Alexander Fleming’s observation of mold killing bacteria led to the creation of penicillin.
- The identification of repetitive DNA sequences paved the way for CRISPR, a groundbreaking gene-editing technology.
Understanding genetics has transformed with the advent of inductive reasoning, which allowed the formulation of the double helix DNA model.
The implications of this have been profound, ranging from forensic science to the treatment of genetic diseases.
Turning our gaze to the skies, astronomers use inductive reasoning to propose hypotheses about celestial phenomena.
By observing light patterns, they infer the existence of new planets and the behavior of distant stars.
The power of inductive reasoning in scientific exploration cannot be overstated.
It’s the engine driving our inquiry into the unknown, pushing the boundaries of what we believe is possible.
As we continue our pursuit of knowledge in filmmaking and beyond, inductive reasoning remains a vital tool, illuminating our path forward in the ever-expanding field of discovery.
What Is Inductive Reasoning – Wrap Up
We’ve seen how inductive reasoning is a cornerstone of progress in fields as diverse as physics and filmmaking.
It’s our ability to draw on previous experiences and project into the future that has led to some of the most groundbreaking discoveries of our time.
From the vast expanse of space to the microscopic intricacies of our DNA, inductive reasoning guides our quest for knowledge.
It’s what propels us forward, ensuring that every new insight builds on the last, paving the way for future innovations that we can only begin to imagine.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Inductive Reasoning?
Inductive reasoning is a logical process in which multiple premises, all believed to be true, are combined to obtain a specific conclusion.
It involves making generalized deductions from observed patterns or examples.
How Is Inductive Reasoning Used In Scientific Discovery?
Inductive reasoning in scientific discovery involves formulating hypotheses and theories based on observed phenomena.
By analyzing patterns and data, scientists can propose explanations that can be tested and refined.
Can You Give An Example Of Inductive Reasoning In Physics?
Yes, Einstein’s development of the theory of relativity is a prime example.
Observing the consistency of the speed of light and the peculiarities of motion, Einstein used inductive reasoning to propose new concepts about time and space.
What Role Did Inductive Reasoning Play In Medical Advancements?
Inductive reasoning was crucial in the development of penicillin.
After noticing that certain mold cultures killed bacteria, Alexander Fleming inferred the possibility of an antibacterial agent, leading to the discovery of penicillin.
How Has Inductive Reasoning Impacted Genetics Research?
The formulation of the double helix DNA model by Watson and Crick was guided by inductive reasoning.
They drew conclusions about DNA structure by analyzing X-ray diffraction patterns and the chemistry of nucleotides.


