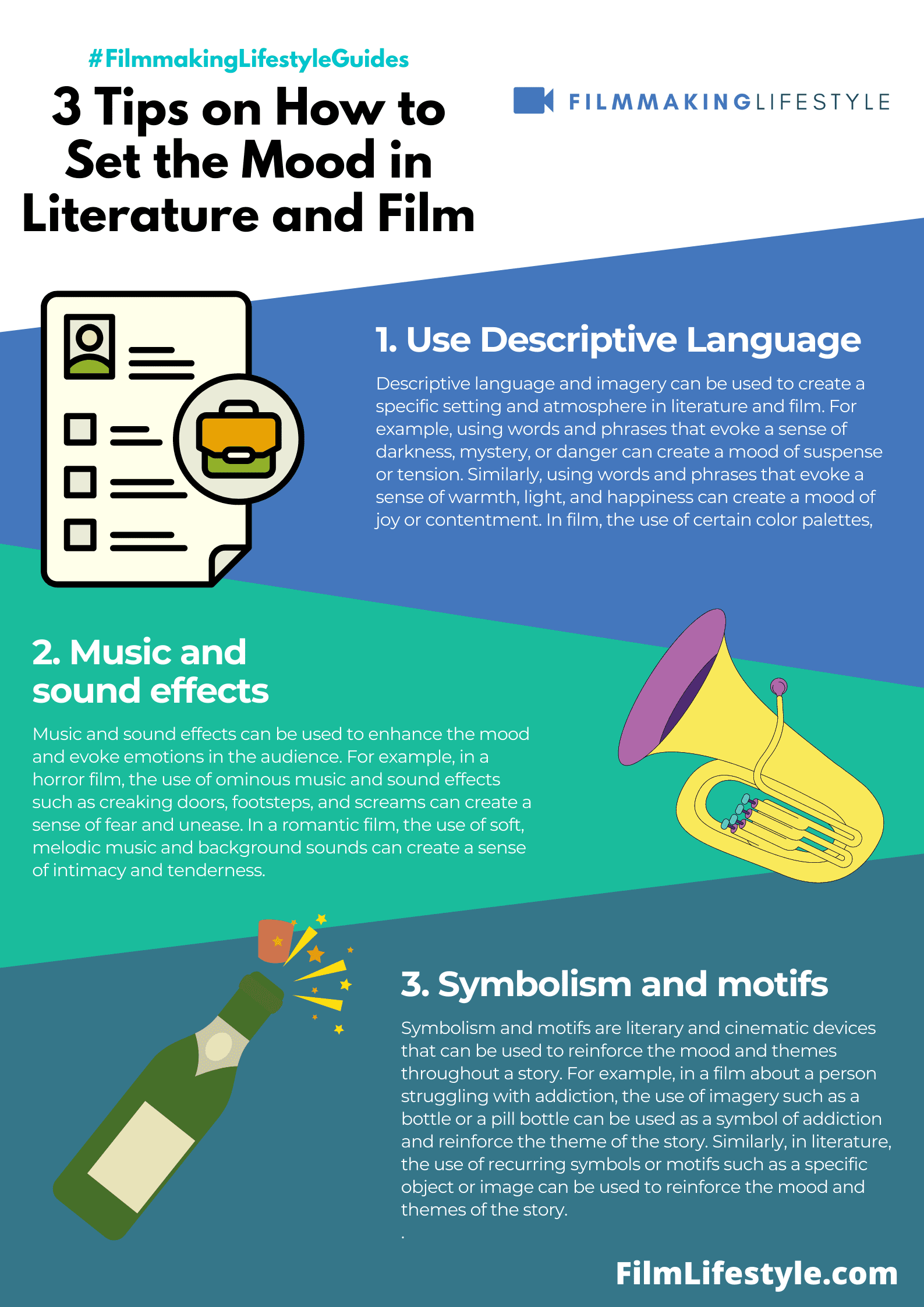
Mood is the overall feeling of a piece of writing or film. In other words, mood is the feeling that is created in the reader or viewer by the work.
Perhaps you’ve experienced a song putting you in a good mood or a bad mood. A movie or book can do the same thing, of course.
Mood can be caused by many things:
- The subject matter of a story.
- The language used by writers and directors (for example, it might be obscure or simple).
- The actions and interactions of characters.
- The tone of the work (the attitude toward the subject matter), which is one of the nuances of mood.
In simple terms, mood is the overall feeling of the writing. Simply put, a sentence with a sad mood might say, “It’s raining outside.”
A sentence with a happy mood would say, “The sun is out!” In more complex terms, it may be helpful to think about how writers use language elements in order to create mood.
Sometimes, it may be more interesting to look at how the characters’ actions and dialogue make the mood.
Let’s take a look.
What Is mood
What Is mood?
Mood is the feeling that pervades a literary work or a film. It may be conveyed through the setting, characterization, syntax, dialogue, narration and imagery.
The term “mood” may also be used to describe visual elements of films as well as music and sound effects.
In this context, mood is often referred to as “mood music.” Mood elements in films are designed to complement and enhance onscreen action and emotion.
In literature and film, mood is conveyed through many different forms such as character development, dialogue and narration.
Mood’s the subtle undertone that colors our daily experiences, whether we’re soaking in the joy of a sunny day or wrestling with the gloom of a stormy night.
It’s a complex cocktail of emotions, setting the stage for how we interpret the world around us.
In this article, we’ll unpack the intricacies of mood, exploring its psychological roots and the factors that shape it.
We’re diving deep into understanding why mood matters and how it influences our behavior, decision-making, and overall well-being.
Keep reading to discover the power of mood in our lives.
The Definition Of Mood
When we jump into the essence of mood, it’s crucial to understand that mood is more than just a fleeting feeling.
It encompasses an enduring state of mind that can significantly color our experiences and interactions.
From the ambiance of a room to the narrative tone of a film like The Godfather, mood shapes the fabric of the stories we see and the environments we inhabit.
Our mood is subtly woven into the backdrop of our daily lives.
It often goes unnoticed, yet it’s pivotal in charting the course of our day.
Much like a skilled director sets the tone in a movie, our mood quietly directs the action and drama of our real-life encounters.
It’s a complex tapestry made up of various emotional threads, each contributing to the overarching theme of our current state.
In our discussions about mood, we frequently come across terms like ‘atmosphere’ and ‘ambience’.
These words help illustrate how mood can almost be tangibly felt in different settings:
- Atmosphere – The pervading tone or mood of a place, situation, or work of art.
- Ambience – The character and atmosphere of a place.
Understanding mood in the context of filmmaking opens up a new dimension.
We manipulate lighting, music, and pacing to craft a compelling mood that resonates with audiences.
Such elements are meticulously woven together to enhance the narrative, much as they are in our daily lives.
Mood is not a static entity.
It is dynamic and responsive, influenced by external factors like weather or internal shifts like our health or thoughts.
Recognizing this fluidity is essential in harnessing mood’s potential in creative endeavors, whether we’re behind the camera or facing life’s various scenes.
The Psychological Roots Of Mood
Understanding the underlying psychological mechanisms of mood can be as captivating as the narrative twists in a masterful film.
At its core, mood is often a reflection of the interplay between our emotions and thoughts.
It’s a complex, persistent state that may emanate from our personal narrative, much like the thematic essence of a film.
Mood isn’t just a spontaneous emotional response.
It’s sculpted by cognitive processes which include our perceptions and evaluations of events around us.
Recognizing the psychological foundations of mood is akin to understanding the script of a film, where character motivations and story arcs drive the plot forward.
The intricate framework of our mood is influenced by numerous factors –
- Biological elements such as neurotransmitter levels and hormonal imbalances,
- Psychological influences like stress, anxiety, or the aftermath of a poignant scene,
- Sociocultural elements encompassing societal norms and interpersonal dynamics.
Films like Eternal Sunshine of the Spotless Mind unveil the complexity of human emotion and the depths of our psyche.
They allow us to explore the nuances of mood and its psychological roots.
The characters’ moods shift and evolve, underscoring how external events and internal reflections are inexorably linked.
By delving into psychology, we gain insight into how moods can shape our narratives, both in life and on the screen.
Mood is the unsung hero of our daily lives, subtly directing our actions and reactions without the grand fanfare of more overt emotions.
As filmmakers and creatives, we must be attuned to the subtle hues of mood that color our work and the experiences of our audience.
Just as a cinematographer carefully selects the lighting to set the right tone for a scene, we continuously adjust our mental spotlight to illuminate the most beneficial state of mind.
Factors That Shape Mood
Understanding what creates and alters mood is pivotal in both our personal lives and creative endeavors.
Our mood is constantly influenced by a dance of variables that surround and inhabit us.
Physiological factors play a significant role.
These include our brain chemistry, hormones, and overall physical health.
Our brain releases different chemicals like serotonin and dopamine, which significantly impact how we feel and respond to our environment.
Psychological elements cannot be overstated.
Stress, self-esteem, and past experiences are configured into this mix, each affecting how we perceive the world.
Resilience in the face of challenges can either strengthen or destabilize our mood states.
Social interactions and relationships also sway our mood.
Positive engagements can uplift us, whereas conflicts or social isolation might lead us to feel down.
As filmmakers, understanding the importance of social dynamics can inform character development and narrative arcs in films like The Godfather or Casablanca.
Environmental influencers include:
- The weather and seasons,
- Colors and lighting,
- Space and design.
These elements not only shape mood in our living spaces but are also carefully crafted in film settings.
Consider the bleak colors in Schindler’s List or the stark contrasts in Sin City, both anchoring the viewer firmly within the intended atmosphere.
Cultural and societal norms mold our moods by dictating what is acceptable or expected in a given context.
The collective mood of a society can have a profound effect, as seen in films that explore cultural revolutions or societal breakdowns.
Finally, our behavior and activities have a direct impact.
Choosing to engage in exercise or pursue a hobby can improve our mood substantially.
In filmmaking, this parallels the way a montage scene can signify a character’s growth or emotional journey.
The Importance Of Understanding Mood
Understanding mood goes beyond mere emotional awareness.
It’s essential for effective communication and storytelling.
In filmmaking, the ability to craft scenes that viscerally connect with audiences hinges on our grasp of mood dynamics.
We see this exemplified in the nuanced atmospheres of films like The Godfather or Inception, where mood is as influential as the characters themselves.
Recognizing the elements that contribute to mood allows us to engineer experiences that resonate.
Here are some key focal areas:
- Lighting and color palettes – they set the tone of each scene,
- Music and sound design – they underscore emotional undercurrents,
- Setting and time of day – they offer context that influences mood.
We can’t overlook the importance of cultural and social contexts either.
The mood in a scene reflects not only the director’s vision but also collective sentiments.
Consider the cultural impact of a film like Black Panther.
Its mood captured a moment in history, speaking to social movements and bringing together a global community.
The same principles apply when marketing our films.
We create promotional content that establishes the mood, aiming to capture the essence of the film and entice potential audiences.
This requires a strategic blend of visuals, copy, and timing.
We aren’t just selling a film; we’re inviting viewers into a unique emotional landscape.
To truly master storytelling, we must become adept at manipulating mood.
It’s the undercurrent that guides the narrative flow and stakes.
Master filmmakers often leave a signature mood imprint on their work – think Tim Burton’s gothic fantasy or Wes Anderson’s quirky melancholy.
In practice, mood informs every creative decision we make.
It’s the silent partner to our plot, directing the subtext and shaping audience reactions without uttering a single word.
And in our ever-evolving digital landscape, harnessing the power of mood has never been more critical.
The Influence Of Mood On Behavior And Decision-making
Mood profoundly affects how we make decisions and interact with the world around us.
It can skew our perception, influence our interactions and even dictate the choices we make.
In the realm of filmmaking, being aware of the mood’s power is crucial for shaping narratives that resonate with audiences.
From the films we choose to watch to the stories we’re drawn to create, mood steers us, often subconsciously.
Decisions in the director’s chair, from casting to set design, are tinted with the brush of the prevailing mood.
For example, the grim ambiance of Blade Runner 2049 informs every aesthetic decision, from the dystopian landscape to the subdued performances.
On a behavioral level, mood impacts how we interpret dialogue, scenes, and characters.
Let’s consider these aspects:
- Mood influences the tone of dialogue – does a character’s line come off as sarcastic or genuine?
- It dictates the pacing of scenes – should this moment be frantic or introspective?
- Character decisions feel authentic if their mood aligns with their actions, thereby affecting audience empathy.
Cutting-edge research supports the instrumental role of mood in decision-making.
Findings suggest that positive moods lead to more flexible thinking and openness to innovative ideas.
On a set, this might manifest as improvisation that leads to a film’s most memorable moments.
Conversely, negative moods can result in more critical and analytical thinking.
Directors and editors might harness a scrutinizing mood to make precise cuts and decisions that tighten the narrative threading through a film.
This ensures each scene serves its intended purpose within the story’s larger tapestry.
The Impact Of Mood On Overall Well-being
Our mood not only shapes the experiences we create but also profoundly influences our overall sense of well-being.
It acts as a barometer for our mental and emotional health, often signaling when something is off-balance.
When we’re in a good mood, we’re more likely to feel motivated and engaged with our surroundings, an essential factor when directing a scene or planning a shoot.
Conversely, a sour mood can sap our motivation and cloud our judgment, potentially leading to less inspired decisions on set.
Positive moods have been linked to numerous benefits for our well-being.
Individuals often experience:
- Enhanced creativity and problem-solving abilities,
- A stronger immune system,
- Higher levels of energy and concentration,
- Improved relationships and social interactions.
These advantages can be crucial when faced with the complexities of film production, where creative thinking and stamina are key.
In contrast, negative moods can contribute to a range of adverse health outcomes.
They’re associated with:
- Increased stress and anxiety,
- A higher risk of developing depression,
- Reduced cognitive function,
- Impaired decision-making.
Recognizing how moods can influence health assists us in identifying the need for self-care and adjustments in our creative process.
Monitoring our mood becomes particularly vital when working on intensive projects like feature films where the stakes are high and the pressure is on.
also, understanding mood’s pervasive impact can lead to better team dynamics on set.
When we’re tuned into the mood of our fellow crew and cast members, we can foster a more supportive and productive environment.
This awareness can precipitate necessary changes, whether it’s offering a word of encouragement or adjusting the day’s schedule to maintain positive momentum.
The intricate relationship between mood and well-being is indispensable knowledge for us in the film industry.
It equips us with the foresight to navigate the ebb and flow of emotional states, ensuring we can always bring our best selves to the creative table.
What Is Mood – Wrap Up
We’ve seen how mood intricately weaves into the fabric of our daily lives influencing our decisions, creativity, and interactions.
It’s clear that a deep appreciation of mood’s power can enhance our storytelling, particularly in film, where it can make or break the connection with our audience.
By staying attuned to the shifts in our emotional states, we can better manage our well-being and foster an environment that nurtures innovation and collaboration.
Let’s harness the subtle yet profound impact of mood to bring out the richness in our narratives and the authenticity in our characters.
Together, we can create stories that not only entertain but also resonate deeply with viewers, leaving a lasting impression long after the credits roll.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Influences Our Mood On A Daily Basis?
Various factors shape our mood daily, including physiological conditions, psychological state, social interactions, environment, cultural background, and behaviors.
Each of these elements can significantly affect how we feel and react to our surroundings.
Why Is Understanding Mood Important In Filmmaking?
Understanding mood is vital in filmmaking because it affects perception, interactions, choices made by directors, and the audience’s empathy with the narrative.
Being attuned to mood nuances can inform character development, enhance storytelling, and resonate with viewers’ emotions.
How Does Mood Affect Decision-making In Film Directors?
Mood influences a film director’s decision-making by impacting their perception and choices within the creative process.
Positive moods can lead to more flexible and innovative thinking, while negative moods may result in a more critical and analytical approach to decision-making.
Can Mood Impact Audience Interpretation Of A Film?
Yes, mood can heavily impact how an audience interprets dialogue, scenes, and character actions.
It affects the empathetic connection an audience develops with the narrative, shaping their overall film experience.
What Is The Relationship Between Mood And Well-being In The Film Industry?
Mood has a direct effect on well-being in the film industry, influencing motivation, judgment, and decision-making.
Positive moods are associated with increased creativity and problem-solving, whereas negative moods can lead to stress and impaired cognitive function.
Understanding mood is essential for self-care and maintaining a productive on-set environment.


