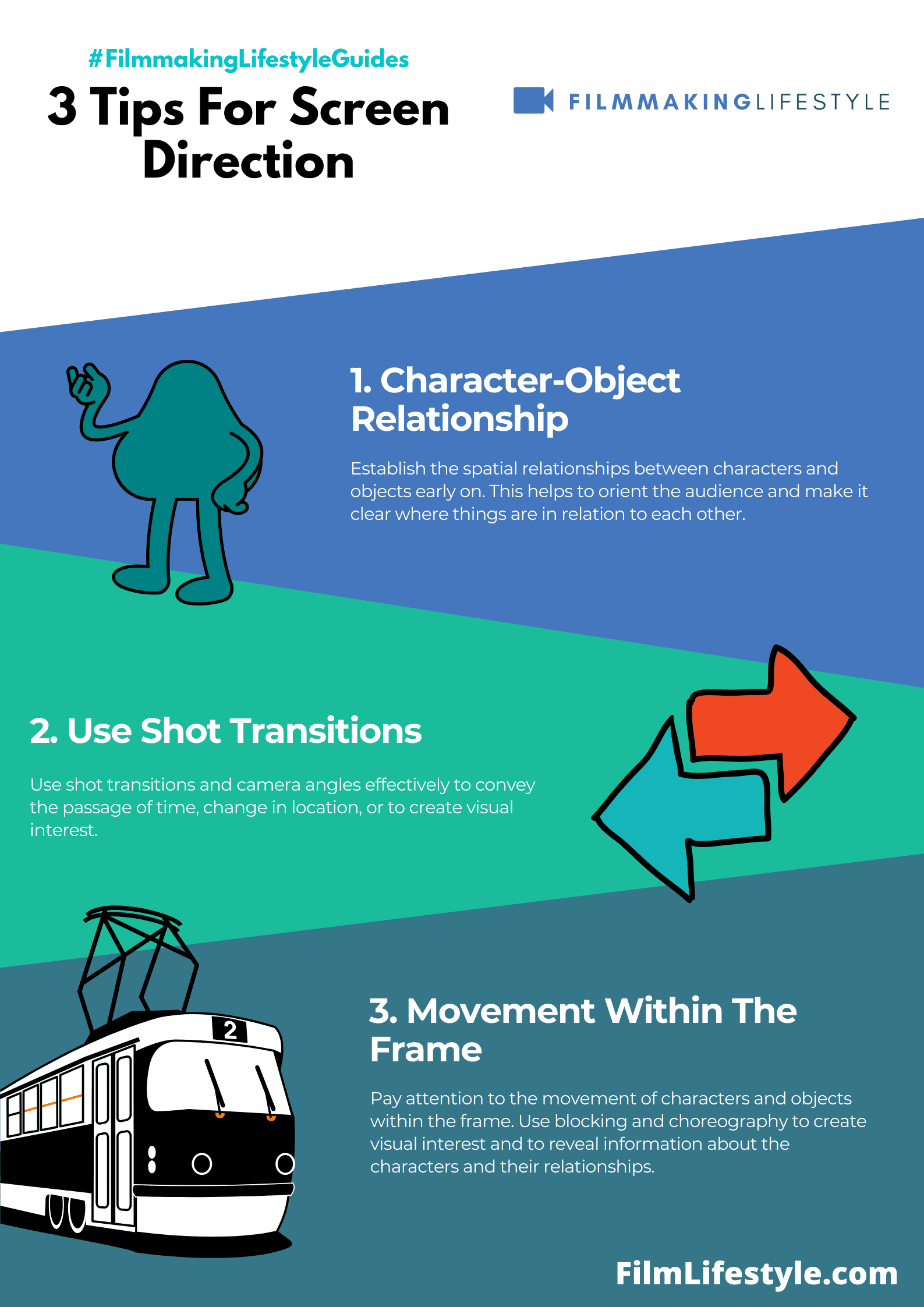
Screen direction, or eye-line, is the perspective that a movie scene or TV show aims to give the audience. Essentially it’s the way the camera or set of characters look at one another in a scene.
One character may be looking at another, or a character may be looking out of a window. This can be important for creating an atmosphere in a scene and subliminally directing the audience to look at something in particular.
What Is screen direction
What Is screen direction in film?
Screen direction in film is the order in which action takes place, because a story can be told from more than one point of view.
Telling a story from multiple points of view can help the audience understand all sides of a conflict and make their own judgments about what’s happening.
However, not all stories are suited for this technique. Some stories are better told through the eyes of one main character.
Telling a story from multiple points of view starts with choosing the order in which you want to tell the story. That order is called screen direction. It’s also known as camera angle or POV (point of view).
The most common technique is to decide on screen direction after you’ve written the script and have a clear idea of where you want to start. However, it’s possible to make this decision while writing the script if you know your characters and plot well enough.
In the world of film, screen direction isn’t just about left or right—it’s a storytelling powerhouse.
We often don’t realize it, but the way characters move across the screen can deeply influence our perception of the narrative.
It’s a subtle art that guides viewers’ eyes and emotions, seamlessly shaping the story without a single word.
We’re diving into the nitty-gritty of screen direction, unraveling its importance in creating a cohesive visual experience.
Whether it’s maintaining continuity or building tension, mastering screen direction is crucial for filmmakers.
Stick with us as we explore how this fundamental aspect of filmmaking keeps audiences engaged and drives the story forward.
What Is Screen Direction In Film?
Screen direction in filmmaking refers to the visual movement or path that the viewers’ eyes follow when watching a film.
It’s a crucial element that contributes to the storytelling process by directing the audience’s attention in a deliberate manner, using the movement of objects or characters across the screen.
This movement can be left to right, right to left, towards the camera, or away from it.
Each of these directions has a subtle psychological impact, making screen direction a potent tool in a filmmaker’s toolkit.
For instance, characters moving from left to right are often perceived as moving forward in a narrative, signaling progress.
When considering the elements of screen direction, we focus on several key aspects:
- The rule of thirds, crucial for composition,
- The 180-degree rule, essential for spatial consistency,
- The use of lead room to anticipate movement.
It’s important to maintain screen direction for continuity’s sake.
Audiences expect a seamless visual experience, and sudden changes in screen direction can lead to confusion.
For example, if a character exits screen left and enters the next scene from the right without explanation, it may disorient the viewer.
Films like The Graduate Use screen direction to craft visual metaphors and drive the narrative forward.
Directors have the power to create tension or relaxation through the careful orchestration of visual cues and in-camera direction, often without the audience even realizing it.
By consciously controlling screen direction, filmmakers ensure that each scene flows into the next, creating a cohesive and immersive cinematic experience.
We recognize these patterns subconsciously, and they play a significant role in how we interpret and engage with films.
The Importance Of Screen Direction In Visual Storytelling
Understanding screen direction is tantamount to mastering the language of film.
It’s about using visual cues to guide the audience, ensuring they’re not just passive viewers but active participants in the narrative journey.
Manipulating screen direction is a powerful storytelling device within a filmmaker’s toolkit.
It enhances the narrative by aligning the audience’s perspective with the intended emotional and psychological beats of the story.
Subtle changes can suggest a character’s progression or regression, leading viewers to invest more deeply in the plot.
In action sequences, screen direction creates a seamless flow, making each cut imperceptible.
Imagine Mad Max: Fury Road without a keen attention to screen direction – the chaos would overwhelm the spectator, leaving them lost amidst the stunning visuals.
Screen direction also functions effectively in:
- Establishing spatial orientation – offering clues about where characters are in relation to each other and their environment,
- Reflecting character dynamics – indicating relationships and power structures through positioning and movement,
- Creating visual metaphors – utilizing motion to represent abstract concepts like time or change.
When screen direction syncs with the cinematography and editing, the result is a visual narrative that feels both intuitive and innovative.
The visual language becomes so fluid that viewers may not even consciously notice the techniques employed, but they will certainly feel the impact.
Directors and cinematographers collaborate to craft these visual narratives.
By employing techniques such as the rule of thirds and the 180-degree rule, they can anchor the audience’s gaze and create a sense of balance and focus within the frame.
By consciously weaving screen direction into the tapestry of filmmaking, we shape not only how a story is told but also how it’s experienced.
The eyes of the viewers So become an extension of the camera lens, moving through the narrative space as intended by the storytellers.
Continuity And Screen Direction: How It Keeps The Story Cohesive
Continuity in film is the backbone that keeps the narrative seamless.
It’s what allows the audience to follow a story without getting jolted by inconsistencies or confused by the spatial relationship between characters and their environment.
Screen direction plays a pivotal role in maintaining this continuity.
When characters move from one shot to the next or when action sequences unfold, keeping the screen direction consistent helps the viewer understand the progression without feeling disoriented.
In dynamic scenes, mismatched screen direction can break the viewer’s immersion.
To prevent this, we rely on tools like match-on-action and the 180-degree rule – ensuring that the direction of movement or the gaze of a character is maintained from shot to shot.
Key techniques used in maintaining screen direction include:
- Eyeline matching,
- Action axis consistency,
- Directional lighting cues.
The intricate dance of camera and character movement is choreographed to complement the storyline.
Movies like Mad Max: Fury Road expertly guide the audience through chaotic action while maintaining clear spatial orientation, thanks to masterful screen direction.
eventually, screen direction isn’t just about where characters are looking or moving.
It’s an essential component that supports the story’s believability and helps the audience stay engaged in the world we’ve created on screen.
Creating Tension And Emotion Through Screen Direction
The manipulation of screen direction is key to amplifying tension and emotion in film.
Subtle changes in on-screen spatial relationships can convey a multitude of feelings, from intimacy to isolation.
Consider a scene where two characters are facing off.
By employing tight close-ups with minimal background context, we create a sense of claustrophobia and intensity.
On the other hand, placing characters on opposite sides of the frame evokes a feeling of distance or conflict.
Directional changes in movement can also impact the viewer’s emotional response.
Here’s how we can use movement to enhance the narrative tension:
- Sudden shifts from left to right can jolt viewers and create unease.
- Consistent movement in one direction can build anticipation or suggest progression.
Films like Gravity manipulate screen direction to establish a sense of disorientation in the vastness of space.
Our perception of up and down is challenged, adding to the film’s tension and the emotional plight of the characters.
Contrastingly, the smooth, horizontal tracking shots in La La Land support the film’s romantic and dreamy atmosphere.
These shots guide the viewer through the scene, mirroring the characters’ emotional journey.
Incorporating opposing movement within a scene can also heighten drama.
We see this technique in The Dark Knight during intense chase sequences where the hero and villain move in contrary directions, enhancing the narrative conflict.
The strategic use of screen direction does more than just guide the audience’s eyes.
It evokes the very essence of the story we’re telling, without the viewers consciously realizing how it’s affecting them.
Through these visual cues, we tap into the shared human experience, creating a bond between the film and the audience that transcends the screen.
Mastering Screen Direction: Tips For Filmmakers
Screen direction is more than just a technical component of filmmaking – it’s a storytelling tool.
To guide our characters through their emotional journeys, we must understand how to use screen direction creatively.
Incorporating the 180-degree rule ensures spatial consistency and helps maintain audience engagement.
We avoid confusing viewers by keeping the action on a single side of an imaginary line.
Our choice of camera angles can dramatically alter the perception of a scene.
High and low angles confer power and vulnerability, respectively, while neutral angles offer an objective point of view.
We Use movement to its full potential – consistent motion in one direction suggests stability and progression.
In contrast, erratic movement or sudden shifts in screen direction can suggest tension or disorientation.
The rule of thirds is crucial for composing shots with depth and interest.
By aligning our subjects with these intersections, we create dynamic scenes that are pleasing to the eye.
Consistency in screen direction is key – continuity errors can pull the audience out of the story.
We pay close attention to ensure that screen direction is matched from shot to shot.
Let’s not forget the psychological impact of screen direction:
- Movement from left to right often feels more natural and positive given our cultural biases toward reading and progress.
- Conversely, right to left can create a sense of unease and can be used to unsettle the audience.
Integration of these elements allows us to convey a cohesive story without relying on dialog or exposition.
We leverage the visual language of film to show, not tell, our story.
As we advance in our filmmaking journey, we collect a toolbox of screen direction techniques.
These tools empower us not just to direct the eye but to stir the heart and engage the mind.
What Is Screen Direction In Film – Wrap Up
We’ve explored the intricacies of screen direction and its pivotal role in storytelling within film.
Mastering these techniques is essential for filmmakers aiming to deliver a visually cohesive and emotionally engaging narrative.
By understanding the subtle yet powerful language of screen direction, we can guide our audience through a story seamlessly, ensuring they remain fully immersed from beginning to end.
Let’s harness the power of screen direction to create films that resonate deeply and leave a lasting impression on viewers.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Screen Direction In Film?
Screen direction in film refers to the way in which movement and position are orchestrated on screen to guide the viewer’s eye and enhance storytelling.
Why Is The 180-degree Rule Important In Filmmaking?
The 180-degree rule is important in maintaining spatial consistency between shots, helping the audience understand where characters and objects are in relation to each other, and keeping them engaged in the story.
How Do Camera Angles Affect A Scene’s Perception?
Camera angles can significantly impact the viewer’s interpretation of a scene, with high angles often signifying weakness or vulnerability, and low angles suggesting power or dominance.
What Does Consistent Motion In Screen Direction Signify?
Consistent motion in screen direction tends to suggest stability and progression, portraying a sense of normalcy or advancement in the storyline.
How Can Erratic Movement Or Sudden Shifts In Screen Direction Impact A Scene?
Erratic movement or sudden shifts in screen direction can create tension or disorientation, often used to reflect a character’s confusion or to build suspense in the narrative.
What Is The Rule Of Thirds In Film Composition?
The rule of thirds is a compositional technique that divides the frame into a grid with two horizontal and two vertical lines, placing important visual elements along these lines or at their intersections to create a more dynamic and visually interesting shot.
How Does Screen Direction Affect The Psychological Impact Of A Scene?
Screen direction can have a psychological impact; for instance, movement from left to right is often perceived as positive and natural, while motion from right to left can evoke feelings of unease or negativity.
Why Is Consistency In Screen Direction Vital?
Consistency in screen direction is critical to avoid continuity errors, ensuring the visual elements align from one shot to the next, thereby maintaining the audience’s immersion and belief in the story.
How Does Mastering Screen Direction Benefit A Filmmaker?
Mastering screen direction techniques allows a filmmaker to convey a cohesive and engaging story visually, effectively communicating emotional and intellectual aspects to the audience.


