Realism In Art is the representation of life, objects and people as they are. Realism is a style of painting that uses realistic representation to depict natural human emotions and scenes as if they were actually happening.
The aim of realism in art is to portray the world around us in a realistic way.
Realism in painting is a term used to describe the value of using deeply subjective perceptions and express them on canvas or paper with exactness, clarity and honesty.
Realism in art is also known as naturalism or veristic. This means that it uses real life objects to make a work of art which reflects the truth about its subject matter.
Realism In Art
What Is Realism In Art?
A realistic painting is one which shows what the artist sees as he looks at a real object or scene. The artist’s eye may be an artist’s eye, but it is not necessarily the same as yours.
If you look at a real object and see something very different from what the artist sees, you might be able to tell him about it. But if you do not see what he sees, all you can say is that his image is inaccurate.
Realism in painting means using real objects and scenes as models for making pictures of them; having a vision of things as they really are; and being able to reproduce them faithfully on canvas or paper.
The word “realistic” comes from the Latin res (thing) and situs (place), and means “of place”.
Realism in art is a movement that champions the depiction of everyday life with truthful, unembellished detail.
It’s a mirror reflecting the times, capturing the ordinary with extraordinary precision.
Throughout this article, we’ll explore how realism evolved, its key characteristics, and the influential artists who brought it to life.
Stay with us as we jump into the world where art meets reality head-on, and discover why realism still resonates with audiences today.
The Origins Of Realism In Art
Realism in art emerged in the mid-19th century as a direct challenge to the dominant Romantic movement of the time.
Romanticism celebrated emotion, imagination, and the exotic, whereas Realism aimed to represent subject matter truthfully, without artificiality, and avoiding artistic conventions or implausible, exotic, and supernatural elements.
The 1850s, in particular, witnessed the growing frustration with the dramatic subjects and hyperbolic emotions of Romantic painting.
In response, artists began to focus on ordinary people and everyday life, hoping to elevate the mundane to the level of fine art.
Gustave Courbet’s painting The Stone Breakers, created in 1849, epitomizes this shift – instead of idealized heroes, Courbet painted a pair of roadside laborers engaged in backbreaking work.
Key Milestones in Realism:
- 1840s-1850s – Realism takes form, reacting against Romanticism.
- 1855 – Courbet’s Pavilion of Realism, an independent exhibition held outside of the official Paris Salon, lays the groundwork for future movements like Impressionism.
The realist painters held a belief that art should represent our world, with all its grit and beauty, that was radical for its time.
They insisted that truth and accuracy in art could communicate social conditions and human experiences more effectively than the idealized narratives of their predecessors.
This commitment to portraying real life in art can be seen as a precursor to the narrative approaches we take in modern filmmaking, demonstrating the enduring influence of the Realism movement.
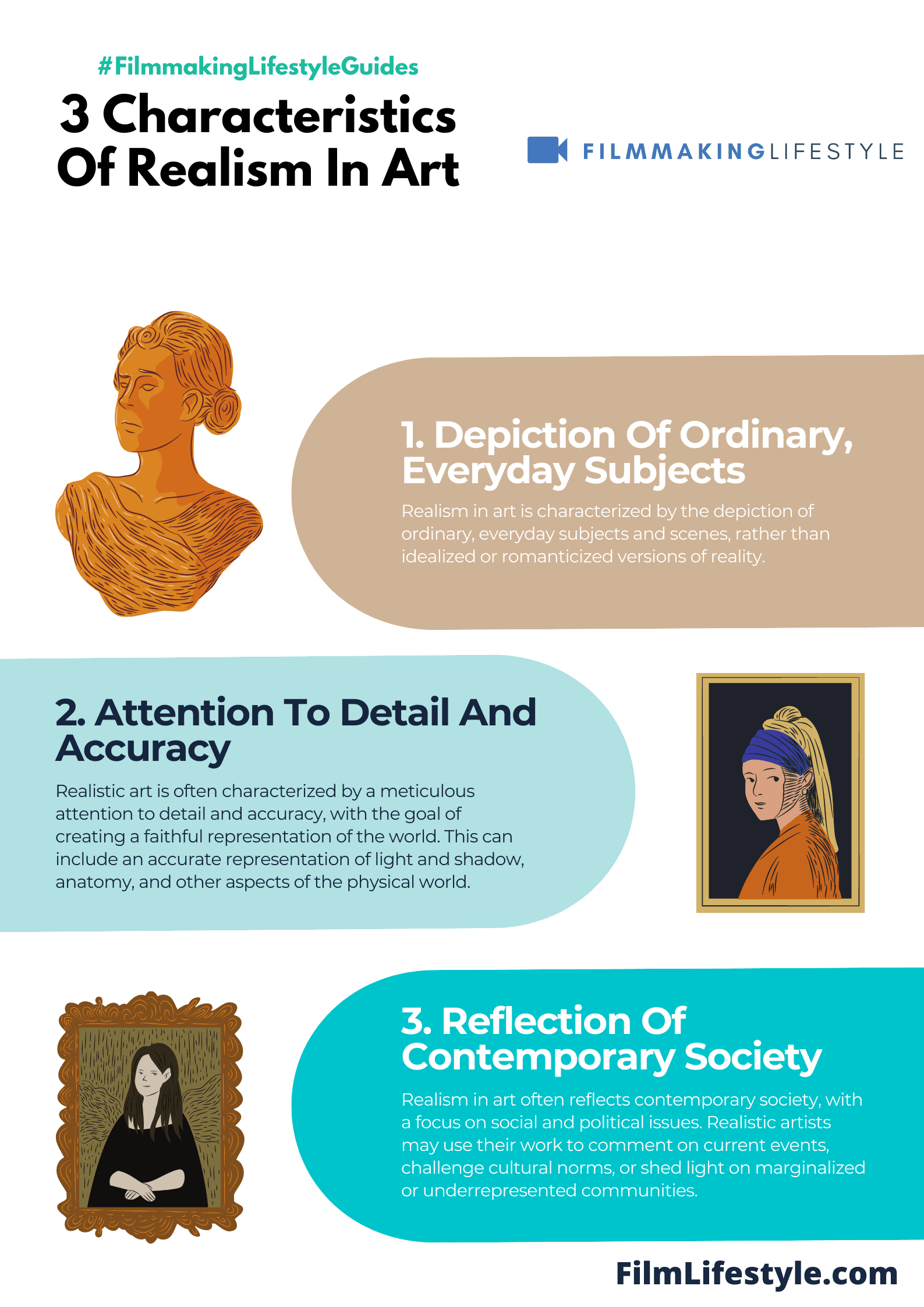
Key Characteristics Of Realism
When discussing the realist movement in art, it’s crucial to understand the defining characteristics that set it apart from other styles.
Realism was grounded in a rigorous approach to depicting everyday scenes with truth and accuracy.
Let’s explore some of these characteristics in detail:
- Truthful representation of ordinary subjects – realist artists chose to portray the world around them without sugarcoating. They selected subjects that were typical, rather than extraordinary.
- Focus on the common and unidealized – Settings and figures were presented without idealization, highlighting the beauty in the mundane.
- Attention to detail – Every element within the composition was rendered with precision and an almost scientific attention to form and color.
Their compositions often featured a strong sense of naturalism, carefully observing and capturing details like light, shadow, and texture.
The candid nature of realist artwork sought to engage viewers with a reflection of their own reality — a stark contrast to the dramatized scenes found in Romanticism.
Realism also embraced the use of plain language in art.
Gestures and expressions were understated, communicating the narrative without theatrics.
Artists like Jean-François Millet, best known for The Gleaners, extended this unembellished approach into the realm of rural life, emphasizing the dignity and hardships of peasant life.
Another aspect that defined realism was its commitment to social commentary and reform.
Through their art, realists often brought attention to social issues and the plights of the working class.
The unvarnished portrayal of these elements catalyzed conversations about the realities of contemporary life they depicted.
In cinematographic terms, realism has translated into a style that leans towards minimalistic production techniques, on-location shooting, and non-professional actors.
These approaches allow filmmakers to craft works that feel more immediate and authentic to the audience, just as realist painters sought to do in their time.
The Influence Of Realism In Art
Realism’s influence extends far beyond the canvas and into various creative realms.
It’s particularly noteworthy how this movement redefined visual storytelling, both in fine arts and filmmaking.
We can’t stress enough the significance of realist techniques in shaping modern-day aesthetics.
Films like The Bicycle Thief stand as monumental testaments to realism’s persistent impact on cinema.
Our understanding and appreciation of these works are deepened by recognizing their roots in the realist tradition.
These nuanced productions pushed audiences to see the world with an unfiltered perspective, fostering empathy and social awareness.
- Realism marinated in the visual arts and spilled over to literature, where authors like Leo Tolstoy crafted narratives steeped in the ordinary.
- In photography, stark images capturing the raw essence of life evoke the realism principle of truth in detail.
- In theatre, plays like A Doll’s House showcase mundane moments that resonate with authenticity and provoke thought.
The seeds sown by realist artists germinated throughout history, influencing successive movements like Naturalism and social realism.
Through their legacy, we recognize crucial elements such as:
- The prioritization of everyday subject matter,
- A focus on social issues and reform,
- The use of minimalistic techniques to achieve an authentic feel.
These principles have been adapted and intertwined into the DNA of contemporary creative expression.
Visionaries in art and film continue to draw on realism’s ethos, seeking to offer a mirror to society – sometimes a flattering reflection, sometimes not, but always striving for an honest portrayal.
Notable Artists Of The Realism Movement
When exploring the Realism movement, it’s essential to recognize the artists who brought this style to prominence through their groundbreaking work.
The Realism movement was ignited by a desire to depict the ordinary with extraordinary accuracy – shunning romanticism and idealization.
- Gustave Courbet – His assertion that paintings must deal with everyday occurrences set a firm foundation for the Realism movement. His iconic works like The Stone Breakers and A Burial at Ornans challenged the status quo and portrayed the rawness of the working class.
- Jean-François Millet – Millet focused on the dignity of peasant life, bringing scenes from rural existence to the forefront of fine art with works such as The Gleaners.
- Édouard Manet – Often considered a pivotal figure between Realism and Impressionism, Manet pushed boundaries with works like Olympia, bridging social narratives and modern techniques.
Realism also thrived beyond the confines of painting, as seen through the lenses of early photographers.
Photographers like Lewis Hine used their cameras as tools for social change, capturing the harsh realities of child labor and industrial environments.
In literature, writers such as Leo Tolstoy and Mark Twain infused their novels with a realist perspective, grounding their stories and characters in the tangible experiences of daily life.
Their narratives had a lasting impact on the cultural dialogues of their time, echoing into the film adaptations of their works.
The legacies of these artists remain vibrant in contemporary culture.
We see their influence in films that shun CGI for authentic locations, in gritty screenplays that reflect the complexities of real-life situations, and in visual compositions that draw the viewer into the narrative, making them a participant rather than just an observer.
Our understanding of storytelling and aesthetics has been immeasurably enriched by the realist ethos, perpetuating a tradition of truth and representation that continues to resonate with audiences today.
Realism’s Impact On Modern Art
The roots of realism in art have deeply influenced modern art forms, and its impact is especially pronounced in the stark, truthful depictions seen in contemporary pieces.
As aficionados of art across all eras, we recognize that the principles of realism continue to thrive in today’s artistic expressions.
Naturalism and authenticity pervade the works of modern artists.
They steer away from idealized images, using bold strokes and unrefined textures to reflect the unembellished aspects of life.
The ethos of realism stretches into the realms of modern painting, sculpture, and even performance art.
In the realm of film, the realist tradition invites audiences to immerse themselves in narratives that strike a chord with real life.
Directors draw upon techniques that mirror those of Courbet and Millet, crafting scenes that underscore raw human emotions and socioeconomic realities.
- Significant Realist Techniques in Film: – Use of natural lighting – On-location shooting – Casting non-professional actors to achieve authenticity.
Films like The Bicycle Thief and City of God offer windows into the everyday struggles and triumphs of ordinary people.
This perspective engages viewers, enabling a connection through relatable experiences, untarnished by the gloss of escapism.
Realism has also altered the course of art education – challenging instructors and students alike to explore honest depictions in their practice.
Academic curricula now often include realist methodologies, equipping the next generation of artists with the ability to capture the world as it truly is.
We teach not only the technique but also the ethos, instilling a respect for the raw and genuine in every stroke and frame.
What Is Realism In Art – Wrap Up
We’ve seen how realism serves as a powerful force in art, capturing the essence of our shared human experience.
It’s shaped not just the visual arts but also the way we tell stories across various media.
By embracing the raw and unfiltered aspects of life, realism continues to challenge and inspire us, offering a lens through which we can view the world in its true form.
Whether we’re admiring a painting, getting lost in a novel, or feeling the grit of a film, realism reminds us of the beauty in authenticity.
It’s a vital tradition that not only reflects society but also influences how we perceive and create art.
As we move forward, we’ll carry the legacy of realism with us, recognizing its enduring impact on our culture and the endless possibilities it presents for future generations of artists.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who Are The Notable Artists Associated With The Realism Movement?
Gustave Courbet, Jean-François Millet, and Édouard Manet are some of the notable artists of the Realism movement who are known for portraying the stark reality of everyday life.
How Has Realism Influenced Literature?
Realism in literature is characterized by writers like Leo Tolstoy and Mark Twain, who grounded their narratives in real-life events and common folk, moving away from romanticized fiction to more authentic storytelling.
What Role Did Realism Play In Photography?
Photographers like Lewis Hine leveraged realism to capture raw and unembellished scenes, such as the harsh conditions of child labor, bringing societal issues into public view and advocating for change.
Can You Mention Some Films That Reflect Realism?
Films such as “The Bicycle Thief” and “City of God” exemplify realism by using natural lighting, on-location shooting, and casting non-professional actors, helping audiences connect with genuine, relatable experiences.
How Has Realism Impacted Modern Art?
Realism has significantly impacted modern art by inspiring artists to incorporate everyday subject matter and authentic portrayals of life into their work, influencing various mediums including painting, sculpture, and performance art.
Is Realism Included In Art Education?
Yes, realism methodologies are often incorporated into academic curricula to help art students learn to accurately capture and represent the world as it is.


