The term gothic art refers to the art of the Middle Ages (c. 500-1500). The term was first used in the early 19th century, when European churches were being restored and refurbished by 19th-century architects.
Gothic architecture is a style of architecture that flourished during the period of Christianization of Europe, from the 5th to 7th centuries.
Although it developed in several centres across Western Europe, it was best known in its final form in France, where it was highly influential and has remained so since.
What Is Gothic Art
What Is Gothic Art?
Gothic art is a style of Medieval Art that developed during the High Middle Ages in the 12th and 13th centuries, originating in the Romanesque period and continued until the Renaissance. It was succeeded by Early Netherlandish painting in the 14th century and by Late Netherlandish painting in the 15th.
The style is named after the Gothic architecture that developed in France during the 12th century, giving rise to such architectural styles as French Gothic architecture and Spanish Gothic architecture.
The term “Gothic art” can also refer to the art of various countries where this style developed, such as Germany, Hungary, Poland and Scandinavia.
Gothic art is a mesmerizing style that revolutionized medieval Europe with its dramatic, intricate beauty.
It’s an art form that evokes emotion and symbolizes the grandeur of its era.
We’ll explore its origins, characteristics, and lasting impact on the art world.
Get ready to jump into the darkly elegant world of Gothic art and discover what makes it truly captivating.
Origins Of Gothic Art
Gothic art emerged as a powerful aesthetic force in the 12th century, rooted deeply in the heart of medieval Europe.
It signified a departure from the rounded arches and heavy solidity of Romanesque architecture, ushering in a new era of pointed arches, soaring vaults, and light-flooded interiors.
We can trace its birth to the Ile-de-France, particularly with the design of the Basilica of Saint Denis – a work largely attributed to Abbot Suger, who sought to create a physical manifestation of divine light and harmony.
This transformative style quickly spread across Europe, morphing to match local tastes and theological visions.
Gothic art wasn’t confined to architectural wonders alone; it permeated various facets of creative expression:
- Sculpture – Svelte figures that seemed to reach for the heavens, adorned the portals of cathedrals,
- Paintings – Evocative works that aligned with the spiritual narratives of the time,
- Stained glass windows – Vivid storytelling through light and color, creating an ethereal atmosphere within sacred spaces.
The distinctiveness of Gothic art lies in its dynamism and emphasis on verticality, embodying a celestial aspiration that could speak to the soul.
As filmmakers and enthusiasts of all things creative, we’re captivated by the Gothic era’s ability to visually narrate complex spiritual and human experiences in stone, glass, and paint.
The dedication to detail within Gothic pieces commands attention, and the harmonious interplay between light and shadow parallels techniques we apply in our own cinematic works.
As we jump deeper into the substance of Gothic Art, its enduring resonance and adaptability become clear, seamlessly infusing modern narratives with medieval mystique.
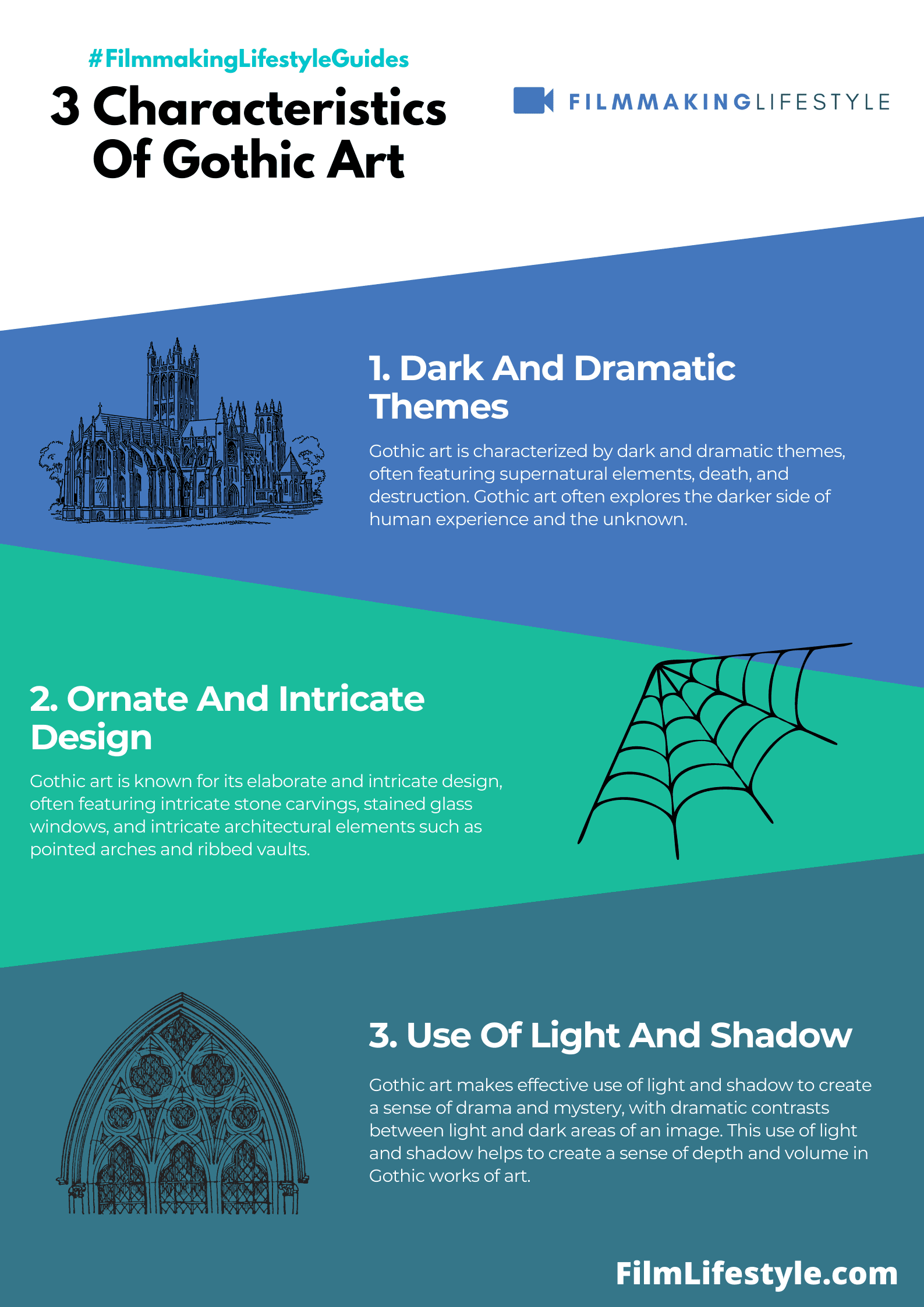
Characteristics Of Gothic Art
Gothic art, with its roots deep in medieval Europe, flourishes through its distinctive characteristics that still captivate us today.
We’ll now jump into these defining features, which collectively offer a glimpse into the artistic language of the era and influence a multitude of modern creative outlets.
Emphasis On Light And Color
We observe that light plays a pivotal role in Gothic art – it’s not just an artistic tool but a symbolic element.
Artists and architects employed light to create an ethereal atmosphere within spaces like Chartres Cathedral, allowing sunlight to pour through colorful stained glass windows.
This interplay between light and color dramatically transformed interiors into divine, radiant settings.
Architectural Innovation
In moving away from the heavy, solid walls typical of Romanesque architecture, Gothic artists embraced structural innovations.
These included:
- Pointed arches – Ribbed vaults – Flying buttresses.
The introduction of these elements not only allowed for taller, more majestic buildings but also ushered in the iconic verticality that defines Gothic architecture.
Consider Notre-Dame de Paris with its remarkable facade, towering spires, and intricate tracery – these features collectively underscore the period’s engineering ingenuity and aesthetic vision.
Ornamentation And Detail
Gothic art’s complexity lies not just in its structure, but also in its rich ornamentation.
We see statues, reliefs, and intricate carvings adorning the exteriors and interiors, depicting a range of subjects from biblical narratives to mythical creatures.
These details provide a deeper insight, often serving as visual sermons that educated and inspired the medieval populace.
Our appreciation of Gothic art continues as we explore its influence on contemporary storytelling and design.
Whether it’s in the realm of film, like the stark, brooding atmosphere of The Hunchback of Notre Dame, or the revival of gothic elements in modern architecture, the legacy of this medieval art form endures through its timeless ability to stir imagination and emotion.
Influences On Gothic Art
Gothic art wasn’t born in a vacuum.
It evolved from a melting pot of cultural and artistic traditions.
Medieval society was a tapestry of religious devotion and burgeoning intellectualism, all of which found expression through the Gothic style.
The Romanesque movement is often seen as the direct predecessor, but Gothic art also drew its flavors from the following:
- byzantine art – with its intricate mosaics and iconography,
- Islamic art – for its geometric patterns and emphasis on light interplay,
- Classical antiquity – where Gothic sculpture found its underpinning in realism and proportion.
The integration of these elements spoke to a world that was expanding its boundaries.
We see an exchange of ideas facilitated by the Crusades and burgeoning trade routes that brings a dynamic quality to the artworks.
Every epoch is defined by its zeitgeist and the Gothic period is no exception.
The rise of universities and a literate clergy meant that scholasticism left its mark on Gothic art.
Artists weren’t just craftsmen; they were intellectuals engaging with theological and philosophical debates of their time.
This intellectual movement drove Gothic art to be more than just decorative – it sought to illuminate and instruct.
Gothic art also reflects a society grappling with the sublime and the divine.
Cathedrals were labyrinths of light and shadow, designed to inspire awe and spiritual contemplation.
We can’t help but see the parallel between the towering spires of a Gothic cathedral and the epic narratives of films like The Lord of the Rings.
Just as these movies transport audiences to another world, Gothic architects aspired to transcend the material and connect the earthly with the celestial.
The influence of natural phenomena on Gothic art can’t be overstated.
With an increased understanding of light, artists could mimic its ethereal qualities through stained glass and open architectural designs.
Light wasn’t just a natural resource; it was a medium for artists to explore – a challenge that filmmakers like us still face today.
Iconography In Gothic Art
Gothic art is rife with symbolic imagery that served both educational and inspirational purposes.
The use of iconography was integral, as many individuals during the Gothic period were illiterate and relied on visual cues to understand complex theological concepts and narratives.
Iconography in Gothic art often drew from biblical tales and the lives of saints.
Figures like the Virgin Mary and Christ were rendered with ethereal grace, surrounded by intricate halos and robes that conveyed their sanctity and importance.
Typical elements included:
- Gargoyles and chimeras – representing the intertwining of the sacred and the profane, as well as serving practical purposes,
- Floral and faunal motifs – symbolizing various virtues, the Garden of Eden, or the frailty of human life,
- The use of light – often depicting spiritual illumination or divine presence.
The portrayal of virtues and vices was also prominent in Gothic sculpture and stained glass.
These were not just simple moral lessons but rich, intricate allegories that engaged viewers in deeper reflection.
The portrayal of virtues was designed to instruct the observer on the path to salvation, while vices acted as warnings against sin.
Medieval bestiaries influenced Gothic iconography significantly.
Mythical creatures such as unicorns, which represented purity, and dragons, which symbolized Satan, permeated Gothic artworks.
These fantastical elements were not mere decoration but carried intense spiritual significance and added layers of meaning to Gothic works.
Stained glass windows, a hallmark of Gothic architecture, served not just as beautiful works of art but as mediums of storytelling and catechism.
Each panel often told a story or highlighted an important Christian doctrine, with vibrant colors and light transforming chapels and cathedrals into transcendent spaces.
Legacy Of Gothic Art
Gothic art has left an indelible mark on various aspects of our cultural history, permeating far beyond its medieval origins.
Its influence can be seen not just in architecture but also in a vast array of contemporary forms ranging from film to literature.
We jump into this vibrant legacy, tracing the threads that connect the past to the present.
One of the most striking impacts of Gothic art is its influence on Romanticism.
The early 19th-century movement drew heavily from Gothic elements, with artists like Caspar David Friedrich showcasing the drama and emotion that Gothic art encapsulated.
Similarly, the intricacies of Gothic design are often mirrored in intricate set pieces and detailed atmospheres of contemporary films.
Crimson Peak and The Name of the Rose are prime examples of this cinematic homage.
We find that the principles of Gothic art have also been weaved into the fabric of storytelling.
The presence of Gothic themes is unmistakable in genres such as horror and fantasy, where the mood and symbolism hark back to the grandeur and spirituality of Gothic cathedrals.
Here are some key components commonly found in such narratives –
- The play of light and darkness – The conflict between good and evil – The elaborate depiction of fantastical creatures.
also, the longevity of Gothic art’s influence is evident in education and public works.
Some universities have adopted Gothic architectural styles for their historic buildings to inspire a sense of awe and continuity.
Oxford and Cambridge are shining examples where the Gothic tradition serves as both a nod to the past and a beacon for the future.
In the realm of video games, the allure of Gothic art manifests through dynamic character designs and immersive world-building.
Titles such as Bloodborne and Darkest Dungeon draw heavily on Gothic motifs to create enthralling experiences steeped in mystery and the macabre.
Though centuries have passed, the legacy of Gothic art is as alive today as it ever was.
It continues to inspire creators across the globe, speaking to the timeless nature of its aesthetics and its power to convey profound human emotions and experiences.
What Is Gothic Art – Wrap Up
We’ve journeyed through the rich tapestry of Gothic art, from its divine architecture to its intricate iconography.
Gothic art’s legacy is unmistakable, resonating through centuries to captivate modern audiences with its profound symbolism and striking aesthetic.
Its influence stretches far beyond its medieval origins, touching the realms of Romanticism and even the digital world of video games.
Gothic art remains a testament to humanity’s enduring quest to blend creativity with spirituality, leaving a mark that’s as indelible as the soaring spires of its cathedrals.
As we reflect on its historical significance, we’re reminded of the power of art to transcend time, speaking to us with the same intensity it did to our ancestors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Gothic Art And When Did It Emerge?
Gothic art is a style of medieval art that developed in Northern France out of Romanesque art in the 12th century, characterized by an emphasis on light and height in its architecture.
Where Can We See An Example Of Early Gothic Architecture?
The Basilica of Saint Denis in France is considered a significant example of early Gothic architecture.
How Does Gothic Art Differ From Romanesque Architecture?
Gothic art differs from Romanesque architecture with its focus on verticality, light, and ornate decoration, moving away from the heavier, more solid forms of Romanesque style.
Did Gothic Art Include Other Forms Besides Architecture?
Yes, Gothic art also encompassed sculpture, paintings, and notably, stained glass windows, which were integral to the aesthetic and function of Gothic cathedrals.
How Did Gothic Art Utilize Light?
Gothic art used light as a symbolic and architectural element to create an ethereal atmosphere within churches, aiming to represent divine presence.
What Influenced The Dynamism Of Gothic Art?
Gothic art was influenced by a variety of elements, including Byzantine, Islamic, and classical art traditions, as well as the intellectual and spiritual ideas of the time.
What Purpose Did Iconography Serve In Gothic Art?
Iconography in Gothic art served educational and inspirational purposes, often depicting biblical tales, the lives of saints, virtues, and moral lessons through symbolism.
How Did Gothic Art Portray Virtues And Vices?
Virtues and vices were commonly portrayed in Gothic sculpture and stained glass as allegorical figures, encouraging viewers to contemplate moral and spiritual values.
What Was The Role Of Stained Glass Windows In Gothic Architecture?
Stained glass windows in Gothic architecture acted as mediums for storytelling and catechesis, illuminating biblical stories and spiritual teachings with light and color.
What Is The Legacy Of Gothic Art In Contemporary Culture?
Gothic art has influenced various aspects of contemporary culture, including Romanticism, film, storytelling, education, and video games, proving its timeless appeal and resonance.


